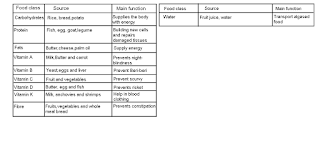
2.1 The Classes of Food
1.The factors affecting a balanced diet include:
(a) Age (b) Body size (c) Gender (d) Occupation (e) Climate (f) State of health
2.All the classes of food are also called nutrients as they contain substances that are needed by our body.
3.Nutrition is the process of obtaining and using nutrients from food.
4.Vitamins are needed in small amounts to keep us healthy.
5.Minerals play a vital role in regulating many body functions.
 |
| Table 2.1 Minerals |
6. Fibre is made up of cellulose and cannot be digested.
7.Cellulose is a long chain of linked sugar molecules that gives wood its remarkable strength. It is the main component of plant cell walls, and the basic building block for many textiles and for paper. Cotton is the purest natural form of cellulose. In the laboratory, ashless filter paper is a source of nearly pure cellulose.
8.Fibre helps food to move easily through the alimentary canal.
9.Alimentary canal is the whole passage along which food passes through the body from mouth to anus during digestion.
10.An adult needs at least 6 to 8 glasses of water a day.
11.We can detect the presence of a nutrient or a class of food by using certain reagents in a laboratory.
 |
| Table 2.2 Food tests |
1.Diet is the food and drinks that we consume every day.
2.A balanced diet is a diet that contains all the classes of food in the correct quantities and proportions.
3.The importance of a balanced diet:
(a) To provide enough energy for the daily activities
(b) To maintain good health
4.Factors that must be considered when planning a balanced diet are
(a) age (b) size (c) gender (d) job (e) climate (f) state of health
5.The food pyramid can help you to plan a balanced diet.
The food pyramid is designed to make healthy eating easier. Healthy eating is about getting the correct amount of nutrients – protein, fat, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals you need to maintain good health.
3.The importance of a balanced diet:
(a) To provide enough energy for the daily activities
(b) To maintain good health
4.Factors that must be considered when planning a balanced diet are
(a) age (b) size (c) gender (d) job (e) climate (f) state of health
5.The food pyramid can help you to plan a balanced diet.
 |
| Figure 2.2 The food pyramid |
6.The calorific value or energy value of food is the amount of heat energy released when one gram of the food is burnt completely.
7.The unit of energy in food can be measured in joules or calories.
1 calories (cal.) = 4.2 joules
2.6 Healthy Eating Habits
2.3 The Human Digestive System
1.Digestion is the process of breaking down large insoluble food molecules into smaller soluble food molecules that can be readily absorbed by the body.
2.Digestion occurs in the digestive system.This system consists of the alimentary canal, glands and organs (refer Figure 2.3).
3.Food is broken down into smaller and simpler forms by physical and chemical digestion.
4.Physical digestion includes chewing by the teeth and churning of the food in the stomach .
5.Chemical digestion involves the action of enzymes on food.
6.Enzymes are substances that act as catalysts and usually speed up the chemical reactions in our body.
7.The diseases caused by nutrient deficiency are as follows:
 |
8.A balanced diet contains all food classes in correct quantity and portion to meet the daily energy requirement of the body.
9.A baby requires more protein for growth.
10.Active children require more carbohydrate to produce energy.
11.A person living in a colder climate requires more energy to warm their body.
12.A construction worker uses more energy than an office clerk.
13.The following diagram shows the nutritional fact on a packet of snack.
Calories per serving
Fat (g) 52 (multiple with energy value 52 x 38kJ/g =1976kJ
Carbohydrates 12 (multiple with energy value 12 x 17kJ/g =204kJ
Protein (g) 4 (multiple with energy value 4g x 17kJ/g =68kJ
Note:kJ is kilojoules
Given that the energy value of fats, carbohydrates and proteins are 38kJ/g, 17kJ/g and 17kJ/g respectively.
Calculate the total amount of energy per serving in this packet of snack.
1976kJ + 204kJ + 68kJ =(ANSWER) 2245kJ
14.Digestion is a process in which large food molecules are broken down into smaller molecules so that assimilation can happen.
15.Pathway of food in the digestive system
Food→Mouth(saliva)→Oesophagus(peristalsis)→Stomach→Small intestine→Large intestine(absorption of water)→Rectum(faeces is stored)→Anus(faeces is excreted)
16.(a)In the mouth,amylase enzyme is secreted by the saliva and digests starch into maltose .
(b)In the stomach,protease digests protein into polypeptide.
(c)In the duodenum,
(i)Amylase digests starch into maltose
(ii)Protease digests polypeptide into peptide.
(iii)Lipase digests fats into fatty acid and glycerol.
(d)In the small intestine,
(i)Maltose digests maltose into glucose.
(ii)Protease digests peptide into amino acid
(iii)Lipase digests fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
(e)Based on (d),state the final product of digestion for:
(i)Carbohydrates: Glucose
(ii)Protein: Amino acid
(iii)Fatty acid and Glycerol
2.4 Absorption of digested food
a) Digested food is absorbed in small intestine by villus.
The characteristics of villus to increase the efficiency of the absorption of digested food are:
1.Have a folded surface.
2.The wall is one cell thick.
b) Digested food is absorbed in the blood.
c)Nutrients are transported to the liver and the heart.
d)Nutrients are transported throughout the body by the heart.
e)Absorption of digested food takes place in the small intestine.
f)Villi are tiny hair-like projections inside the small intestine. They increase the surface area for absorption.
2.5 Reabsorption of Water and Defecation
a)Water is reabsorbed in the large intestine.
b)Constipation is caused by the lack of fibre in our diet.
c)Faeces is stored in a part of the large intestine called the rectum.
d)Diarhoea that occurs during cholera infection is life-threatening because it causes the body to lose water excessively thus causing death.
e)Defecation is the process of removing faeces from the body through the anus.
f)Constipation is the condition where defecation is difficult.
g)Ways to overcome constipation:
i)increase the intake of fibre
ii)Drink 6 to 8 glasses of water a day.
 |
| Enzymes in the human digestive system |
 |
| Human digestive system |
1.Good eating habits:
-Eat nutritious
-Eat in moderation
2.Generous distribution of food:
-To the underprivileged
-To the needy
3.Cultural practices in dining:
-Conform to the sensitivities and religious beliefs of different people
Note
1.Rice and fruits have high carbohydrate contents that cause the sugar level in blood to increase. Eating these food can cause diabetes .
2.The balanced diet for different people is different because it is based on gender,body weight and age.
3.The minerals are needed for strong bones and teeth include calcium and phosphorus.
4.Insufficient protein-rich food will cause a person to suffer from kwashiorkor.
5.A good eating habit is chewing food thoroughly before swallowing.
Chapter 3 is coming soon!



No comments:
Post a Comment